The Fire Hazard Identification process is a method of assessing the likelihood, severity and impact of a fire occurring on a vehicle. This process ensures that our Technical Team are armed with all the knowledge they need to design and specify a system to provide you and your business with the most reliable protection.
Our comprehensive Fire Hazard Identification process covers everything from the operating environment to the machine components. A careful examination of ignition and fuel sources highlights areas that are a fire risk, which allows us to ensure that our system design covers these risks.
What Do We Considered in the Fire Hazard Identification Process?
During this process, we consider not only the machine and its configuration and usage, but the environment and human element. Whether the machine will be handling flammable materials, operating in buildings or in the vicinity of hazards and what the cleaning and maintenance schedule of a machine look like all have an impact on the system design.
Machine
Analysis of the machine identifies areas and components that pose a fire risk and require protecting. Careful consideration of components like the engine, belly pan, electric cabling and fuel and hydraulic lines allows our Technical Team to analyse the heat and fuel sources to determine the potential scale and likelihood of fire on each hazard. This identifies the areas that need to be protected.
Environment
The operating environment of a machine can be overlooked, but whether the machine is static or mobile, supervised or unsupervised and whether it operates in a building or in an open area have an impact on the system it needs. Static equipment may require additional manual actuators while machines operators with less supervision may need a sounder beacon.
Human Element
The human element refers to maintenance, cleaning and operation of the machine. Regular cleaning, machine maintenance and work schedule influence the risk of a fire on a machine, and as such must be considered in the Fire Hazard Identification process.
Engine v Full Hazard Protection
Engine Protection
Engine protection, also referred to as volume protection, refers to the design of systems to cover hazards within the volume of the engine compartment. This method of protecting machines means that hazards located outside the engine compartment are not protected. The system design is based on the volume of the protected area, and the amount of agent and number of nozzles required to protect this area.
Full Hazard Protection
On average, over 25% of fires in heavy mobile equipment originate outside of the engine compartment, so neglecting fire hazards outside the engine compartment puts you and your business at risk of fire. This is why Ardent recommends full hazard protection, which considers hazards outside of the engine compartment in addition to those within.
These hazards can include the transmission, battery compartment, belly pan or high-pressure hoses and hydraulic pumps. The fire hazard identification process identifies the areas within the plant that pose a fire risk, and the system design is based on this.
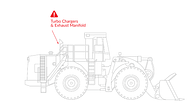
Engine Only Protection
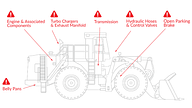
Full Hazard Protection
Fire System Recommendations
This process cumulates in the recommendation of a fire suppression system, including which suppression agent is suitable for the hazards and environment, how much agent is required to offer reliable protection and which areas should be covered by the detection and distribution network.
The Fire Hazard Identification process is a comprehensive process that ensures that every system we specify is fit for purpose. We don't cut corners because we know exactly what it takes to ensure you and your business are fully protected against the risk of fire.

